reading-notes
https://faroukibrahim-fii.github.io/reading-notes/
Game of Greed 3
List Comprehensions in Python
Chances are you’ll use a lot of lists as a Python programmer. While we’re all big fans of for loops (and nested for loops), Python provides a more concise method for handling lists and list comprehension.
In order to keep your code elegant and readable, it’s recommended that you use Python’s comprehension features.
Consider the following example:
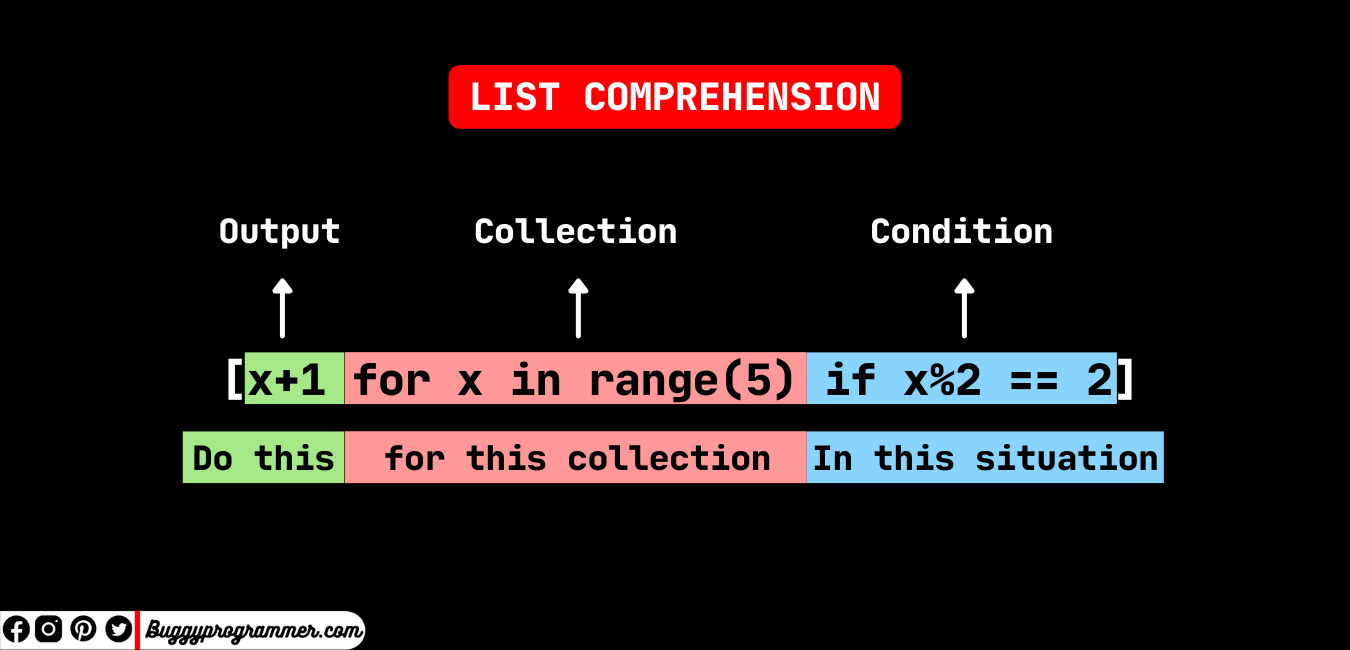
my_new_list = [ expression for item in list ]
You can see from this example that three ingredients are necessary for a python list comprehension to work.
- First is the expression we’d like to carry out. expression inside the square brackets.
- Second is the object that the expression will work on. item inside the square brackets.
- Finally, we need an iterable list of objects to build our new list from. list inside the square brackets.
To understand the list comprehension, imagine it like this: you’re going to perform an expression on each item in the list. The expression will determine what item is eventually stored in the output list.

Notes about Lists Comprehensions
- List comprehension methods are an elegant way to create and manage lists.
- In Python, list comprehensions are a more compact way of creating lists.
- More flexible than for loops, list comprehension is usually faster than other methods.
Create a List with range()
Let’s start by creating a list of numbers using Python list comprehensions. We’ll take advantage of Python’s range() method as a way to create a list of digits.
Example 1: Creating a list with list comprehensions
# construct a basic list using range() and list comprehensions
# syntax
# [ expression for item in list ]
digits = [x for x in range(10)]
print(digits)
Output
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
Create a List Using Loops and List Comprehension in Python
To better illustrate how a list comprehension can be used to write more efficient Python code, we’ll take a look at a side by side comparison.
In the following example, you’ll see two different techniques for creating a Python list. The first is a for loop. We’ll use it to construct a list of the powers of two.
Example 2: Comparing list creation methods in Python
First, create a list and loop through it. Add an expression, in this example, we’ll raise x to the power of 2.
# create a list using a for loop
squares = []
for x in range(10):
# raise x to the power of 2
squares.append(x**2)
print(squares)
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
Output
The same thing can be done using a list comprehension, but with a fraction of the code. Let’s take a look at how to create a list of squares using the list comprehension method.
# create a list using list comprehension
squares = [x**2 for x in range(10)]
print(squares)
Multiplying Parts of a list
What if we wanted to multiply every number in a list by three in Python? We could write a for loop and store the results in a new list, or we could use list comprehensions.
Example 3: Multiplication with list comprehensions
# create a list with list comprehensions
multiples_of_three = [ x*3 for x in range(10) ]
print(multiples_of_three)
Output
[0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27]
By taking advantage of list comprehensions, it’s possible to work on only part of a list. For instance, if you only wanted the even numbers in a given range, you could find them using a filter.
Show the first letter of each word using Python
So far we’ve seen examples of building a list of numbers in Python. Next, let’s try working with strings and the various ways list comprehensions can be used to elegantly handle a list of strings.
Example 4: Using list comprehensions with strings
# a list of the names of popular authors
authors = ["Ernest Hemingway","Langston Hughes","Frank Herbert","Toni Morrison",
"Emily Dickson","Stephen King"]
# create an acronym from the first letter of the author's names
letters = [ name[0] for name in authors ]
print(letters)
Output
['E', 'L', 'F', 'T', 'E', 'S']
Lower/Upper case converter using Python
Using list comprehension to loop through a string in Python, it’s possible to convert strings from lower case to upper case, and vice versa.
Making use of Python’s lower() and upper() methods, we’ll use list comprehension to achieve this common task.
Example 6: Changing a letter’s case
lower_case = [ letter.lower() for letter in ['A','B','C'] ]
upper_case = [ letter.upper() for letter in ['a','b','c'] ]
print(lower_case, upper_case)
Output
['a', 'b', 'c'] ['A', 'B', 'C']
Parsing a file using list comprehension
It’s also possible to read files in Python using list comprehension. To demonstrate, I’ve created a file called dreams.txt and pasted the following text, a short poem by Langston Hughes.
Example 8: Reading a poem with list comprehensions
# open the file in read-only mode
file = open("dreams.txt", 'r')
poem = [ line for line in file ]
for line in poem:
print(line)
Output
Hold fast to dreams
For if dreams die
Life is a broken-winged bird
That cannot fly.
-Langston Hughs