reading-notes
https://faroukibrahim-fii.github.io/reading-notes/
JS Object Literals; The DOM
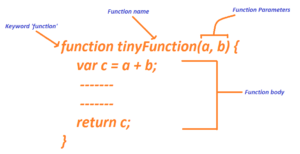
Calling functions that need information
When you call a function that has parameters, you specify the values it should use in the parentheses that follow its name. The values are called arguments, and they can be provided as values or as variables.

Getting a single value out of a function
some functions return information to the code that called them. for example, when they perform a calculation, they return the result.
Getting multiple values out of a function
Functions can return more than one value using an array.
Anonymous functions & function expressions
Expressions produce a value. They can be used where values are expected. If a function is placed where a browser expects to see an expression, then it gets treated as an expression.
Immediatly invoked function expressions
This way of writing a function is used in several different situations. Often functions are used to ensure that the variable names do not conflict with each other.

Variable scope
The location where you declare a variable will affect where it can be used within your code. If you declare it within a function, it can only be used within that function. This is known as the variable’s scope.
Document object model
The Document Object Model (DOM) specifies how browsers should create a model of an HTML page and how JavaScript can access and update the contents of a web page while it is in the browser window.
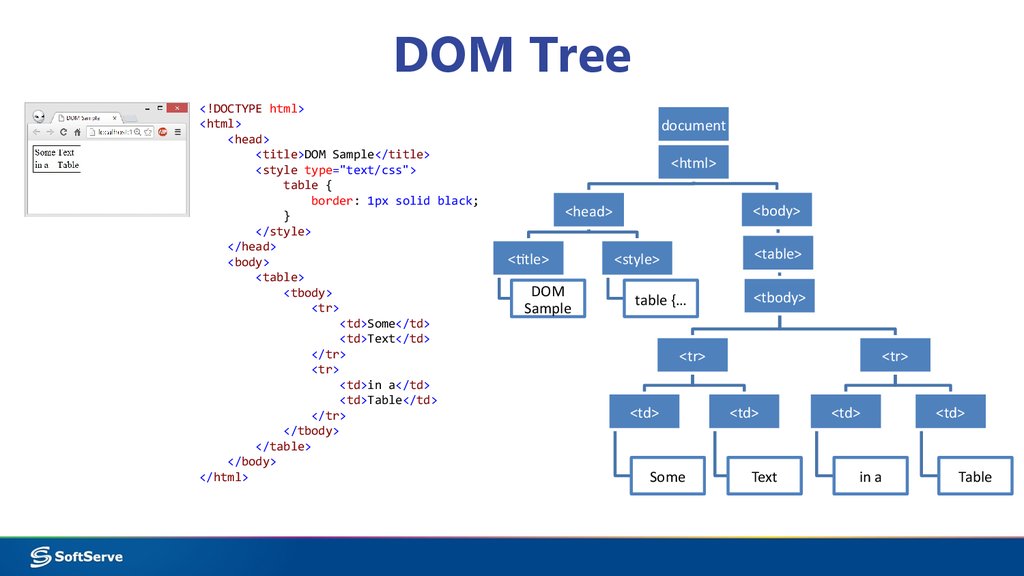
The DOM tree is a model of a web page
As a browser loads a web page, it creates a model of that page. The model is called a DOM tree, and it is stored in the browsers’ memory.
Working with the DOM tree
Accessing and updating the DOM tree involves two steps:
-
Locate the node that represents the elemet you want to work with.
-
Use its text contect, child elements, and attributes.
Step1: Access the elements
Here is an overview of the methods and properties that access elements covered. The first two points are known as DOM queries. The last point is known as traversing the DOM.
- Select an individual element node
Here are the three common ways to select an individual element:
- gerElementById()
- querySelector()
- You can also select individual elements by traversing from one element to another within the DOM.
-
Select multiple elements There are three common ways to select multiple elements.
- getElementsByClassName()
- getElemetsByTagName()
- querySelectorAll()
- Traversing between elements nodes
you can move from one element node to a related elemet node.
- parentNode
- previousSibling / nextSibling
- firstChild / lastChild
Caching DOM queries
Method that find elemets in the DOM tree called DOM queries. When you need to work with an elemet more than once, you should use a variable to store the result of this query.
Methods that select individual elements
getElementById() and querySelector() can both search an entire document and return individual elemts. Both use a similar syntax.

Selecting an element from a nodelist
There are two ways to select an element from a Nodelist:
The item() method and array syntax. Both require the index number of the element you want.
Repeating actions for an entire nodelist
When you have a Nodlist, you can loop through each in the collection and apply the same statements to each.
Adding or removing HTML content
There are two very different approaches to adding and removing content from a DOM tree: the innerHTML property and DOM manipulation.
-
The innerHTML property
-
Approach innerHTML can be used on any element node. it is used both to retrieve and replace content. To update an element, new content is provided as a string. It can contain markup for descendant elements.
-
Adding content To add new content:
- Store new content as a string in a variable.
- Select the element whose content you want to replace.
- Set the element’s innerHTML proerty to be the new string.
-
Removing content To remove all content from an element, you set innerHTML to an empty string. To remove one element from a DOM fragement, you need to provide the entire fragement minus that element.
-
Attribute Nodes
Once you have an element node, you can use other properties and methods on that element node to access and change its attributes.
